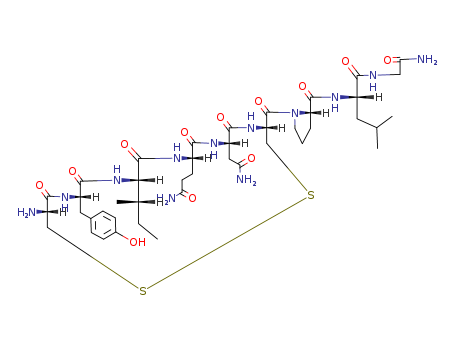
CasNo: 50-56-6
Molecular Formula: C43H66N12O12S2
Appearance: White Solid
|
Receptors |
One specific OT receptor (OTR) has been identified. In humans, the OTR gene is located on chromosome 3 at locus 3p25–26.2, and it encodes a protein of 389 aa residues. In most mammals, the OTR gene consists of three exons while in the human and mouse, an additional intron interrupts the first exon (consequently yielding four exons). Estrogen stimulates OTR expression in the uterus. Complete and/or half-palindromic EREs are found in the promoters of OTR genes. Estrogen-induced OTR expression in the brain is abolished in ER-alpha knockout (KO) mice, whereas the basal OTR expression of the KO mice is similar to that in controls. One OTR has also been found in the holocephalan elephant fish. In elephant fish, a high expression of OTR is found in the muscle and uterus.?OTR couples to Gq/11 and phospholipase C pathways. In addition, OTR activation leads to phosphorylation and activation of the MAPK pathway in uterine myometrial cells. OTR also activates the RhoA-Rho-kinase cascade, which in turn leads to inhibition of myosin phosphatase. The stimulation of nitric oxide production represents an additional signaling pathway to mediate vasodilation, natriuresis, and ANP release. |
|
Agonists and Antagonists |
[Thr4, Gly7]OT and HO[Thr4, Gly7]OT are potent and selective OTR agonists exhibiting negligible vasopressor (V1aR) and antidiuretic (V2aR) activities in rats. In rats, [Thr4, Gly7]OT is more selective to OTR than OT. In humans, HO[Thr4]OT exhibits high affinity and selectivity to OTR, but [Thr4, Gly7]OT is not highly selective.?Atosiban (d[D-Tyr(Et)2 , Thr4, Orn8 ]vasotocin) is a well-known peptidic OTR antagonist, but it also has an affinity for V1aR. The effectiveness of atosiban in delaying premature labor has been demonstrated in many species, including humans. The nonpeptide antagonist SSR126768 has high specificity to OTR. |
|
Indications and Usage |
Oxytocin (OT) is a type of uterine contraction drug and can be derived from the animal posterior pituitary or chemically synthesized. Oxytocin is a uterine contraction drug that is mostly used in late pregnancy induction and stagnant birth due to weak uterine contractions. Suitable for inducing labor and alleviating pain. Commonly used with ergot preparations to be used in inducing labor, expediting labor, and in uterine bleeding due to weak uterine contractions following birth or still birth. Nose drops can be used to promote lactation. |
|
Mechanisms of Action |
Oxytocin does not contain vasopressin and has no pressure-boosting effects. It can be absorbed through oral mucosa, selectively excite smooth uterine muscle, and intensify its contractions. The uterus is most sensitive to oxytocin when in labor (due to increased estrogen secretion), and an immature uterus will not respond to this drug. During early or mid-term pregnancy, the uterus has a relatively low reactivity to oxytocin, which gradually increases during late-stage pregnancy and peaks during labor. Small doses can strengthen the rhythmic contractions of smooth uterine muscles, increase their contractibility, increase their contraction speed, ensure similar contraction characteristics to that of a natural birth, and maintain polarity and symmetry. Thus, it is used clinically to expedite and induce labor. Large doses cause tonic contractions in the uterine muscles, so it is used clinically to burst blood vessels between muscle fibers, prevent postpartum hemorrhage, and ensuring postpartum recovery. It can also promote lactation by causing the breast ducts to contract and expel milk from the breasts, but it cannot increase the lactation amount. |
|
Pharmacokinetics |
Ineffective when taken orally, as it can be damaged by digestive fluids, although it can be absorbed through oral mucosa. 1-3 minutes of venous infusion 0.01 IU can induce physiological uterine contractions (Rhythmic, polar, symmetrical) with a short time span, as its half-life is only 2.5-3 minutes. Large doses cause tonic uterine contractions. |
|
Adverse reactions |
Oxytocin derived from cow or pig’s pituitary occasionally causes allergic reactions, and infusing too quickly may lead to mild vasodilation and hypotension. Patients who suffer from abruptio placentae, heart disease, or enlarged uterus, are over 35 years old, have a history of cesarean section or uterine muscle tumor removal, or are experiencing a breech birth should use with caution. Using oxytocin while experiencing a sacral block may lead to severe hypertension and even cerebrovascular rupturing. Cannot be injected in the same solution with norepinephrine. Incompatible with hydrolyzed proteins. |
|
Contradictions |
Do not use during birth if there are obvious signs of an unsymmetrical head, incorrect fetal position, exposed umbilical cord, prolapse, complete placenta previa, narrow pelvis, or overly intense uterine contractions. Not to be used by patients with overly narrow pelvises, histories of uterine surgery (including C-sections), excessive pains, blocked birth canals, abruptio placentae, or pregnancy poisoning. |
|
Warnings and Precautions |
Dosage and infusion speed must be strictly monitored when used to expedite or induce labor to prevent tonic contractions, which can suffocate the fetus or rupture the uterus. |
|
Description |
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone containing nine amino acids secreted and synthesized by the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus and stored and released by the neurohypophysis. It acts in females by inducing uterine contractions during parturition and stimulating milk ejection by the mammary glands. No actions in males are known. Synthetic derivatives of oxytocin are used to induce labor and for therapeutic abortions. In recent years the safety of oxytocin has been greatly enhanced by the use of continuous maternal and fetal monitoring and by the use of controlled intravenous infusion of the drug. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Oxytocin is a white to yellowish brown powder, hygroscopic, easily soluble in water. It is a synthetic cyclic nonapeptide having the structure of the hormone produced by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland that stimulates contraction of the uterus and milk ejection in receptive mammals. |
|
Originator |
Syntocinon,Sandoz,US,1957 |
|
Uses |
Oxytocin is used as a peptide hormone that acts predominantly as a neurotransmitter; stimulates uterine contraction and lactation, increases Na+ excretion; stimulates myometrial GTPase and phospholipase C. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Oxytocin is a cyclic nonapeptide hormone with amino acid sequence CYIQNCPLG that also acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain; the principal uterine-contracting and milk-ejecting hormone of the posterior pituitary. Together with the neuropeptide vasopressin, it is believed to influence social cognition and behaviour. It has a role as an oxytocic and a vasodilator agent. It is a peptide hormone and a heterodetic cyclic peptide. |
|
Brand name |
Pitocin (Parkdale); Syntocinon (Novartis);Oxytocin;Pituitrin. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Oxytocic |
|
Biosynthesis |
Oxytocin is a cyclic nonapeptide that differs from vasopressin by only 2 amino acids. It is synthesized as a larger precursor molecule in cell bodies of the paraventricular nucleus, and to a lesser extent, the supraoptic nucleus in the hypothalamus. The precursor is rapidly converted by proteolysis to the active hormone and its neurophysin, packaged into secretory granules as an oxytocin-neurophysin complex, and secreted from nerve endings that terminate primarily in the posterior pituitary gland. In addition, oxytocinergic neurons that regulate the autonomic nervous system project to regions of the hypothalamus, brainstem, and spinal cord. Other sites of oxytocin synthesis include the luteal cells of the ovary, the endometrium, and the placenta. |
|
General Description |
Oxytocin (OXT) is a potent natriuretic hormone encoded by the gene mapped to human chromosome 20p13. It is synthesized along with its carrier protein neurophysin I from its inactive precursor prepro-OXT. OXT gene consists of three exons and two introns, where first exon codes for hormone OXT while other exon codes for neurophysin I. |
|
Health Hazard |
Uterine contraction, milk ejection, facilitates sperm ascent in female tract Decreases membrane potential of myometrium, basic metabolic rate, and liver glycogen Stimulates oviposition in hen, releases luteinizing hormone (LH) Increases blood sugar and urinary sodium and potassium |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Oxytocin (OXT) and arginine vasopressin hormone plays a vital role in regulation of water excretion, parturition and lactation. OXT has been implicated in hydromineral homeostasis and vascular and cardiac relaxation. Oxytocin might function as an effective therapeutic for psychiatric diseases, including depression, schizophrenia, anxiety disorders, and autism. OXT has a potential as a marker of autism severity. OXT is an anorexigenic neuropeptide, which is implicated in social cognition and obsessive-compulsive behavior. Plasma oxytocin levels are high in children with Prader-willi syndrome (PWS) compared with unrelated and unaffected siblings. Deficiency of OXT hormone might contribute to pathogenesis of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). |
|
Clinical Use |
Oxytocin is a potent uterine stimulant that is used for the induction and augmentation of labor, antenatal fetal assessment, and control of postpartum hemorrhage. If used improperly, oxytocin can lead to such complications as uterine hypercontractility with fetal distress, uterine rupture, maternal hypotension, water intoxication, and iatrogenic prematurity. These complications can almost always be avoided if oxytocin is given in proper dosages and with careful fetal and maternal monitoring. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous route. Experimental reproductive effects. A pituitary hormone which stimulates uterine contraction and milk production. The principal uterus-contracting and lactation-stimulating hormone of the posterior pituitary gland.Note: Unlike |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
In veterinary medicine, oxytocin has been used for induction or enhancement of uterine contractions at parturition, treatment of postpartum retained placenta and metritis, uterine involution after manual correction of prolapsed uterus in dogs, and in treating agalactia. |
InChI:InChI=1S/C43H66N12O12S2/c1-5-22(4)35-42(66)49-26(12-13-32(45)57)38(62)51-29(17-33(46)58)39(63)53-30(20-69-68-19-25(44)36(60)50-28(40(64)54-35)16-23-8-10-24(56)11-9-23)43(67)55-14-6-7-31(55)41(65)52-27(15-21(2)3)37(61)48-18-34(47)59/h8-11,21-22,25-31,35,56H,5-7,12-20,44H2,1-4H3,(H2,45,57)(H2,46,58)(H2,47,59)(H,48,61)(H,49,66)(H,50,60)(H,51,62)(H,52,65)(H,53,63)(H,54,64)/t22-,25-,26-,27-,28-,29-,30-,31-,35-/m0/s1
We described here the synthesis of oxyto...
S-Acetamidomethyl (Acm) cysteine was fou...
S-protected cysteine derivatives as wel...
The reliability of the (S)-9-fluorenylme...
New methodologies for the construction o...
The detection of thiol functionality and...
The growing interest in synthetic peptid...
The present invention provides a means c...

oxytocin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With isoascorbic acid; In acetic acid;
|
98.5% |
|
With dimethyl sulfoxide; methoxybenzene; trifluoroacetic acid; for 1h;
|
69 % Chromat. |
C90H109N12O14PolS2


oxytocin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With chlorotriisopropylsilane; trifluoroacetic acid; In water; for 0.5h; Rink Amide AM resin
|
85.22% |
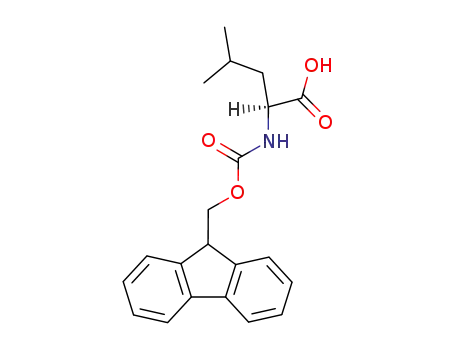
Fmoc-Leu-OH
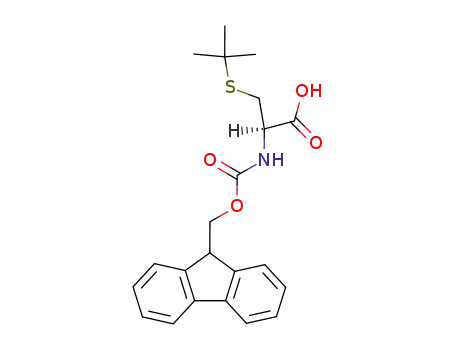
(R)-3-tert-Butylsulfanyl-2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-propionic acid
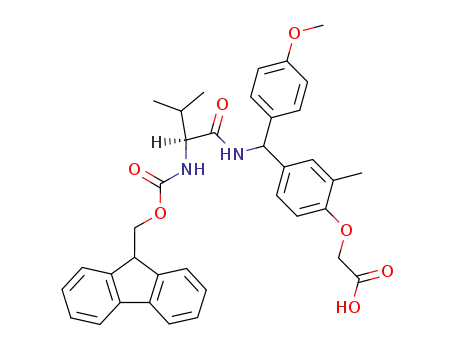
{4-[[(S)-2-(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-3-methyl-butyrylamino]-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-methyl]-2-methyl-phenoxy}-acetic acid
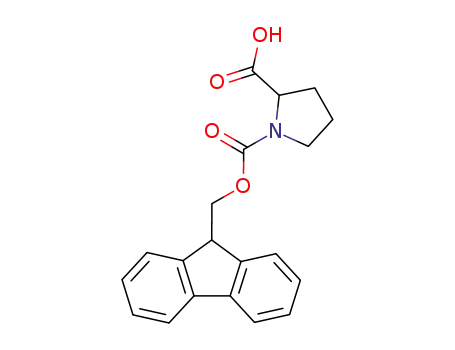
Fmoc-Pro-OH
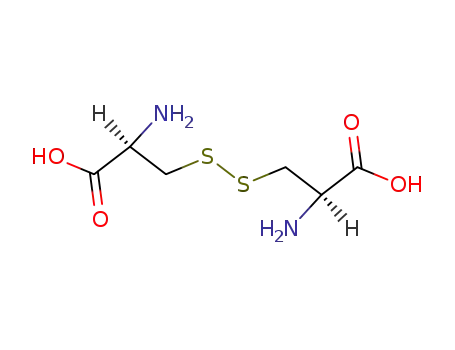
L-cystine
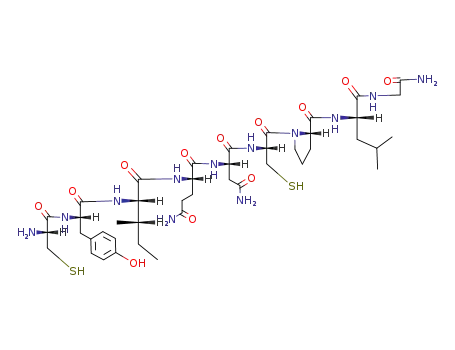
H-Cys-Tyr-Ile-Gln-Asn-Cys-Pro-Leu-Gly-NH2
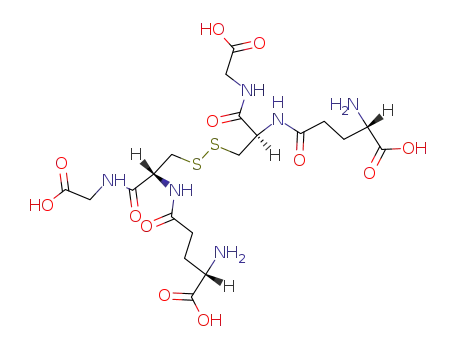
Oxidized glutathione
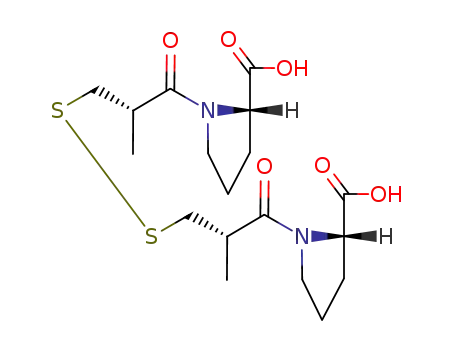
Captopril disulfide